Java - Collections - Hands-on
Learning Objectives
- Understand how to use
List,Set, andMapin Java. - Implement real-world scenarios using Java Collections.
- Practice retrieving, updating, and manipulating collections.
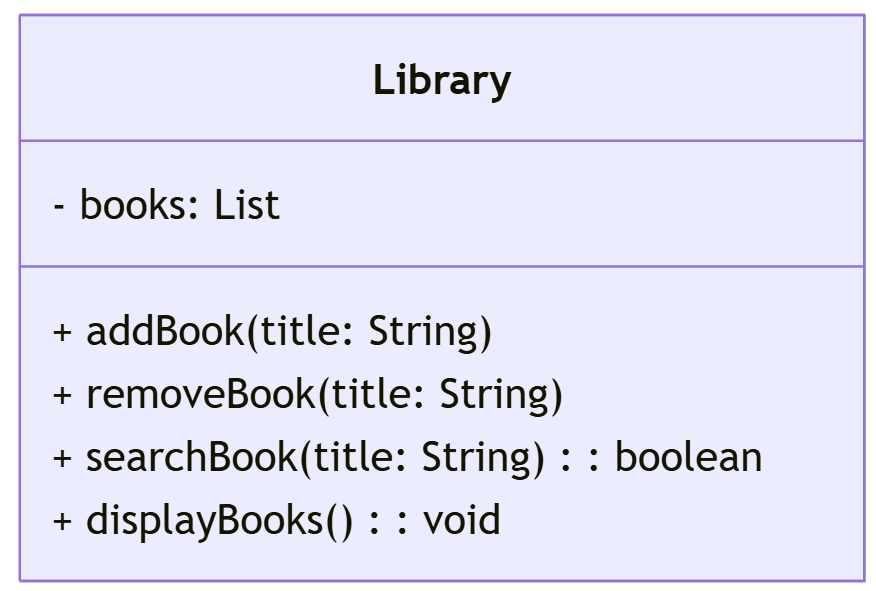
Exercise 1: Managing a Library (Using List)
Problem Statement
A library needs a system to store a list of available books. Implement a List to store book titles and perform the following operations:
- Add books to the library.
- Display all books.
- Remove a specific book.
- Search for a book by title.
Input & Output
Input:
- A list of book titles.
- A title to remove.
- A title to search.
Expected Output:
- The list of books after addition.
- The list of books after removal.
- A message indicating whether a book is found or not.
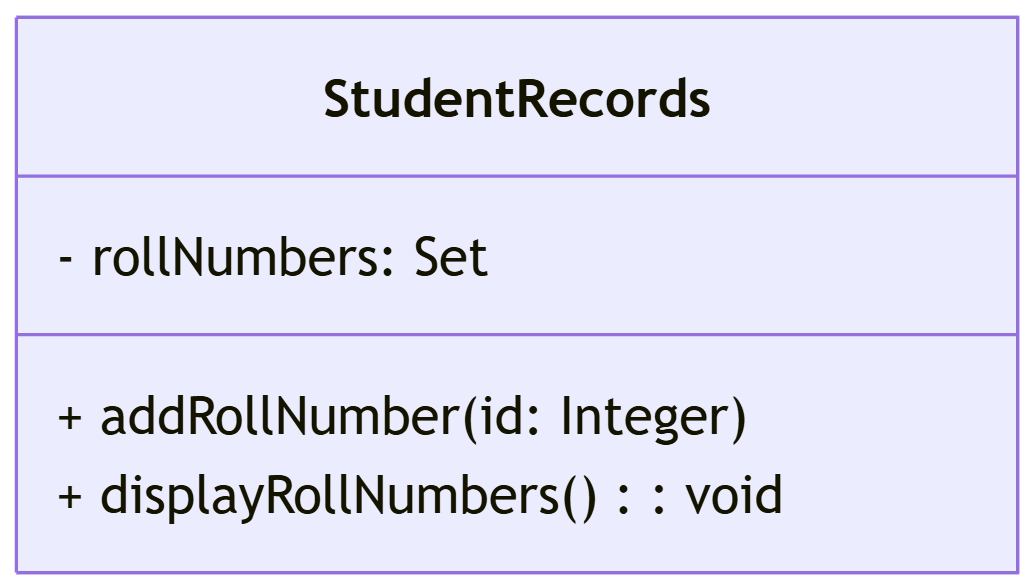
Exercise 2: Unique Student Roll Numbers (Using Set)
Problem Statement
A university stores student roll numbers and wants to ensure that duplicate entries are not added. Implement a Set to store roll numbers and perform the following:
- Add new roll numbers.
- Display all roll numbers.
- Attempt to add a duplicate roll number and observe the output.
Input & Output
Input:
- A set of student roll numbers.
- A roll number to add.
Expected Output:
- The set of roll numbers after adding elements.
- No duplicate roll numbers should be present.
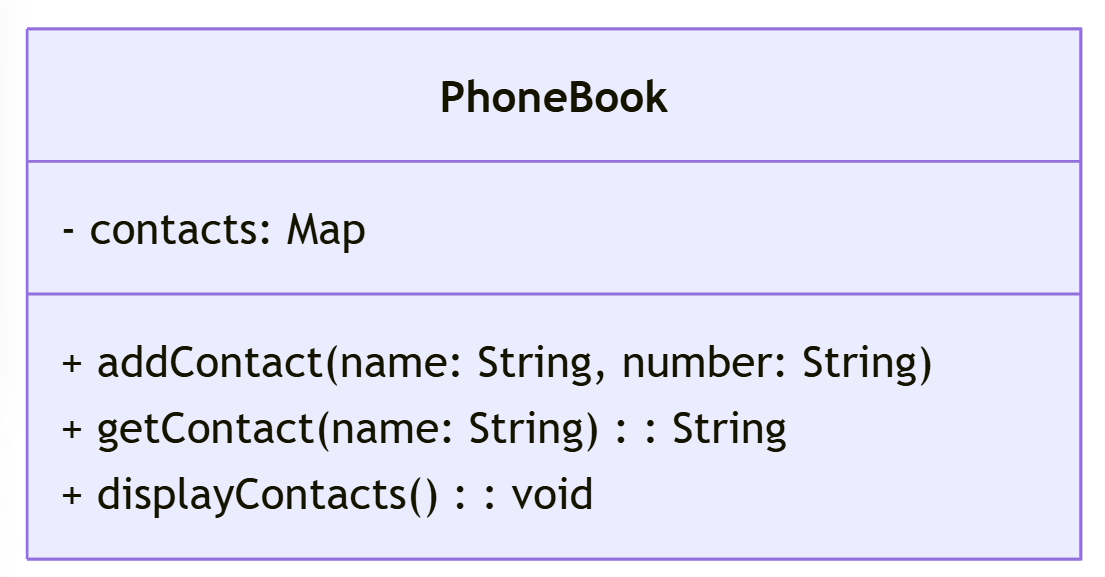
Exercise 3: Phonebook Directory (Using Map)
Problem Statement
A phonebook application stores contacts with names and phone numbers. Implement a Map to store contact details and perform the following:
- Add contacts to the phonebook.
- Retrieve a contact’s phone number using the name.
- Display all contacts.
Input & Output
Input:
- A set of name-phone number pairs.
- A name to search.
Expected Output:
- The list of contacts after addition.
- The phone number associated with a given name.
Java Collections - Sorting Exercises
Exercise 4: Sorting Books by Title (Using Comparable)
Problem
A library needs to sort books by title in alphabetical order. Implement the Comparable interface to allow sorting of book objects.
- Define a
Bookclass with title and author. - Implement the
Comparableinterface to sort books by title. - Add books to a
Listand sort them. - Display the sorted list.
Input & Output
Input:
- A list of books with title and author.
Expected Output:
- The list of books sorted by title.
Exercise 5: Sorting Students by Age (Using Comparator)
Problem
A university maintains student records and needs to sort them by age. Implement the Comparator interface for custom sorting.
- Define a
Studentclass with name and age. - Create a
Comparatorimplementation to sort students by age. - Add students to a
Listand sort them. - Display the sorted list.
Input & Output
Input:
- A list of students with name and age.
Expected Output:
- The list of students sorted by age in ascending order.
Exercise 6: Sorting Products by Price (Using Comparator with Lambda)
Problem
An e-commerce store needs to sort products by price. Use Java 8 lambdas to define the sorting logic.
- Define a
Productclass with name and price. - Use a lambda expression to sort products by price.
- Add products to a
Listand sort them. - Display the sorted list.
Input & Output
Input:
- A list of products with name and price.
Expected Output:
- The list of products sorted by price in ascending order.
| ← Excercise 11 | Next Topic TBD → |
🔗 Related Topics: