Spring > Architecture
Overview
Spring follows a layered architecture, making it flexible and modular. It provides different modules for various functionalities, such as dependency injection, web applications, security, and data access.
Key Layers
Spring is structured into multiple layers:
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Spring Core | Manages dependency injection and bean lifecycle. |
| Spring Web | Facilitates web applications and REST APIs. |
| Spring Data | Supports database operations and ORM. |
| Spring Messaging | Provides integration with messaging systems like JMS and Kafka. |
| Spring Security | Provides authentication and authorization. |
| Spring AOP | Handles cross-cutting concerns like logging and security. |
Spring Core
- Spring Core is the heart of the Spring Framework.
- It provides key functionalities such as bean management and dependency injection.
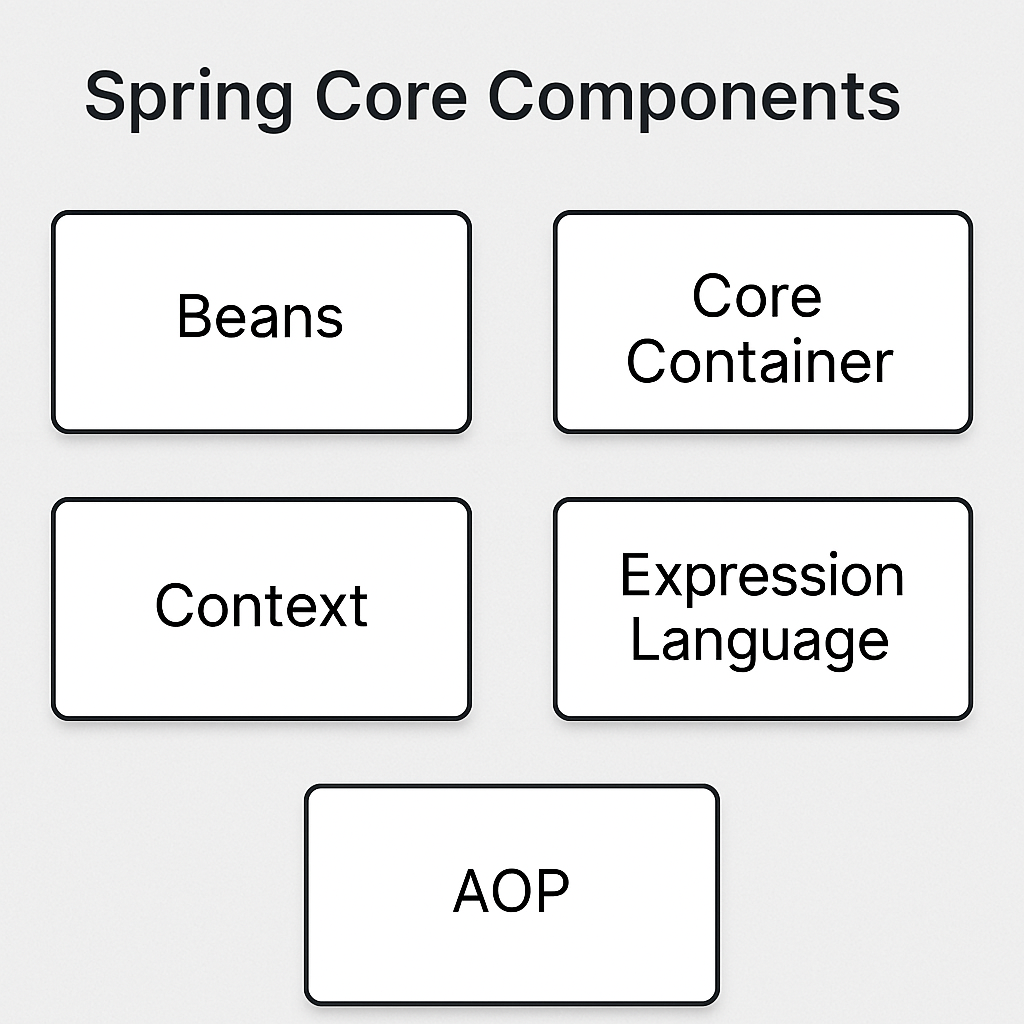
1. BeanFactory
- The simplest Spring container that creates and manages beans.
- Uses an XML configuration or Java-based configuration to define beans.
2. ApplicationContext
- An enhanced version of BeanFactory with additional features.
- Supports event handling, internationalization, and AOP.
- Common implementations:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContextAnnotationConfigApplicationContext
3. Spring Beans
- The objects that Spring manages in its container.
- Defined using
@Componentand@Beanannotations. - Example:
@Component public class MyBean { public void show() { System.out.println("Hello, Spring Bean!"); } }
4. Dependency Injection (DI)
- A way for Spring to provide required dependencies automatically.
- Types:
- Constructor Injection
- Field Injection (
@Autowiredannotation)
5. Spring Expression Language (SpEL)
- Used to retrieve values dynamically within Spring.
- Example:
@Value("#{systemProperties['user.name']}") private String userName;
6. Event Handling
- Enables different parts of an application to communicate.
- Example:
public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent { public MyEvent(Object source) { super(source); } }
7. Resource Management
- Simplifies access to files and resources.
- Example:
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("config.properties");
Conclusion
Spring’s layered architecture makes it flexible, modular, and easy to use for various application types, from monolithic enterprise systems to cloud-native microservices.
| ← Spring Introduction | Spring Modules → |
🔗 Related Topics: